5. RMM Cold and Warm boot design
This section covers the boot design of RMM. The below diagram gives an overview of the boot flow.
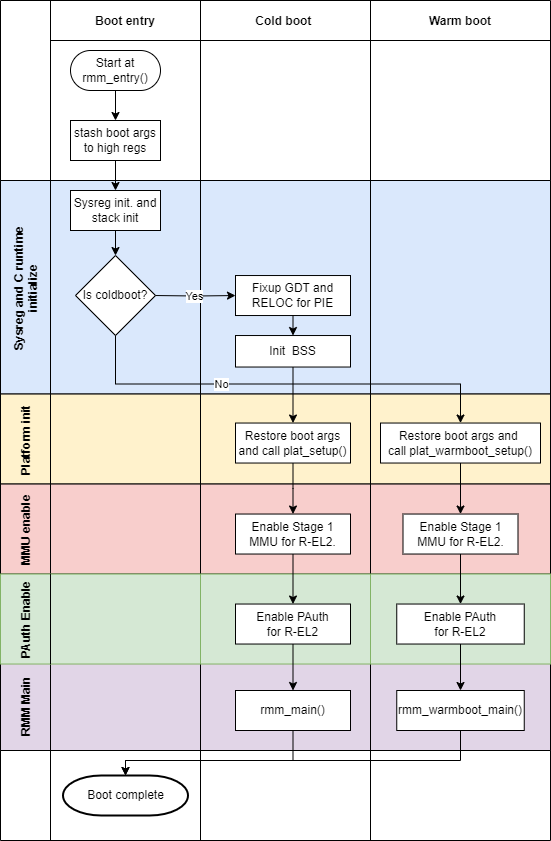
Both warm and cold boot enters RMM at the same entry point
rmm_entry(). This scheme simplifies the
RMM-EL3 communications interface. The boot args as specified by boot
contract are stashed to high registers.
The boot is divided into several phases as described below:
Sysreg and C runtime initialization phase.
The essential system registers are initialized.
SCTLR_EL2.Iis set to 1 which means instruction accesses to Normal memory are Outer Shareable, Inner Write-Through cacheable, Outer Write-Through cacheable.SCTLR_EL2.Cis also set 1 and data accesses default to Device-nGnRnE. The cpu-id, received as part of boot args, is programmed totpidr_el2and this can be retrieved using the helper functionmy_cpuid(). The per-CPU stack is also initialized using the cpu-id received and this completes the C runtime initialization for warm boot.Only the primary CPU enters RMM during cold boot and a global variable is used to keep track whether it is cold or warm boot. If cold boot, the Global Descriptor Table (GDT) and Relocations are fixed up so that RMM can run as position independent executable (PIE). The BSS is zero initialized which completes the C runtime initialization for cold boot.
Platform initialization phase
The boot args are restored to their original registers and plat_setup() and plat_warmboot_setup() are invoked for cold and warm boot respectively. During cold boot, the platform is expected to consume the boot manifest which is part of the RMM-EL3 communications interface. The platform initializes any platform specific peripherals and also intializes and configures the translation table contexts for Stage 1.
MMU enable phase
The EL2&0 translation regime is enabled after suitable TLB and cache invalidations.
PAuth enable phase
Disable API, APK Trap, to allow PAuth instructions access from Realm without trapping. Initialize APIA Keys to random 128-bit value, Enable PAuth for R-EL2.
RMM Main phase
Any cold boot or warm initialization of RMM components is done in this phase. This phase also involves invoking suitable EL3 services, like acquiring platform attestation token for Realm attestation.
After all the phases have completed successfully, RMM issues
RMM_BOOT_COMPLETE SMC. The next entry into RMM from EL3 would be for
handling RMI calls and hence the next intruction following the SMC call
branches to the main SMC handler routine.
6. RMM-EL3 communication specification
The communication interface between RMM and EL3 is specified in RMM-EL3 communications interface specification in the TF-A repository.